OH technology against bacteria: Tests
Much of the pathogenic microorganisms are part of the family of bacteria. The physical characteristics of bacteria are divided into two groups:
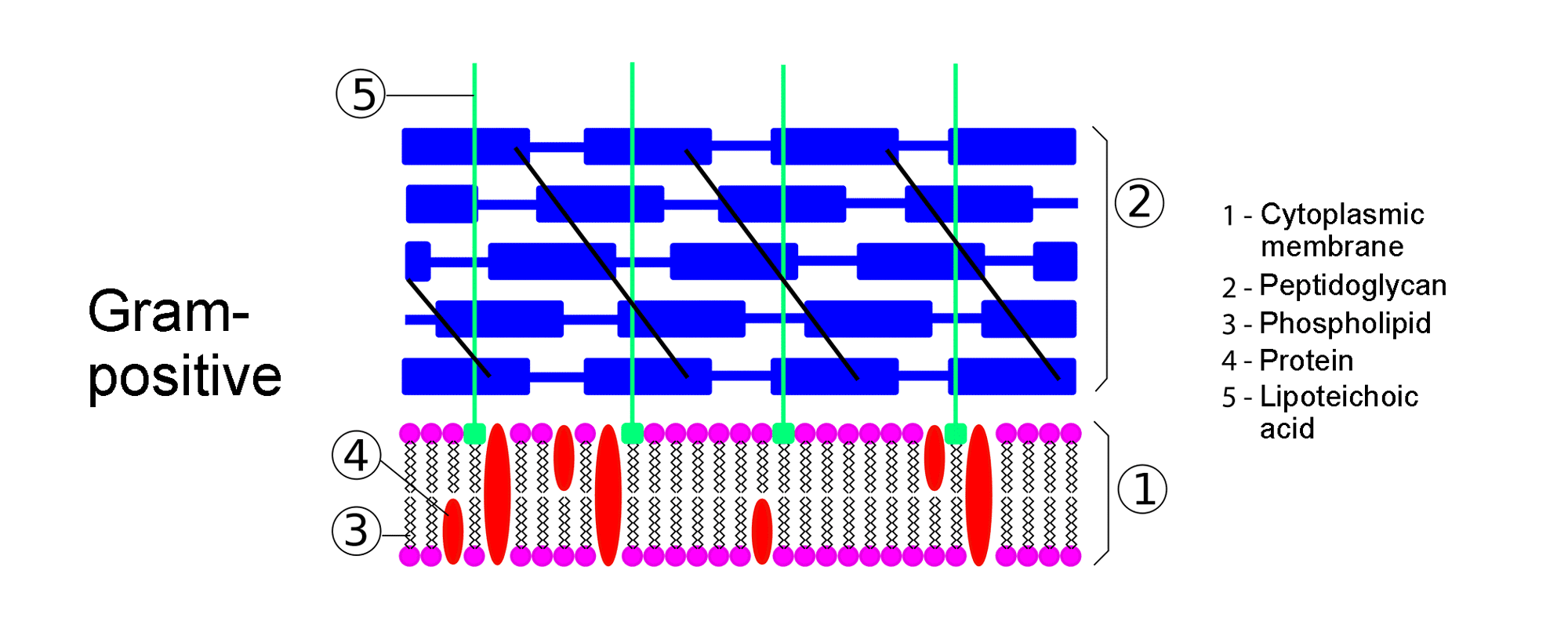
- Bacterium Gram “+”: It is characterized by having two layers on the wall of the bacterium: The external cell wall crossed by protein chains and lipoteicoic acids (among others) and the cytoplasmic membrane (internal wall).
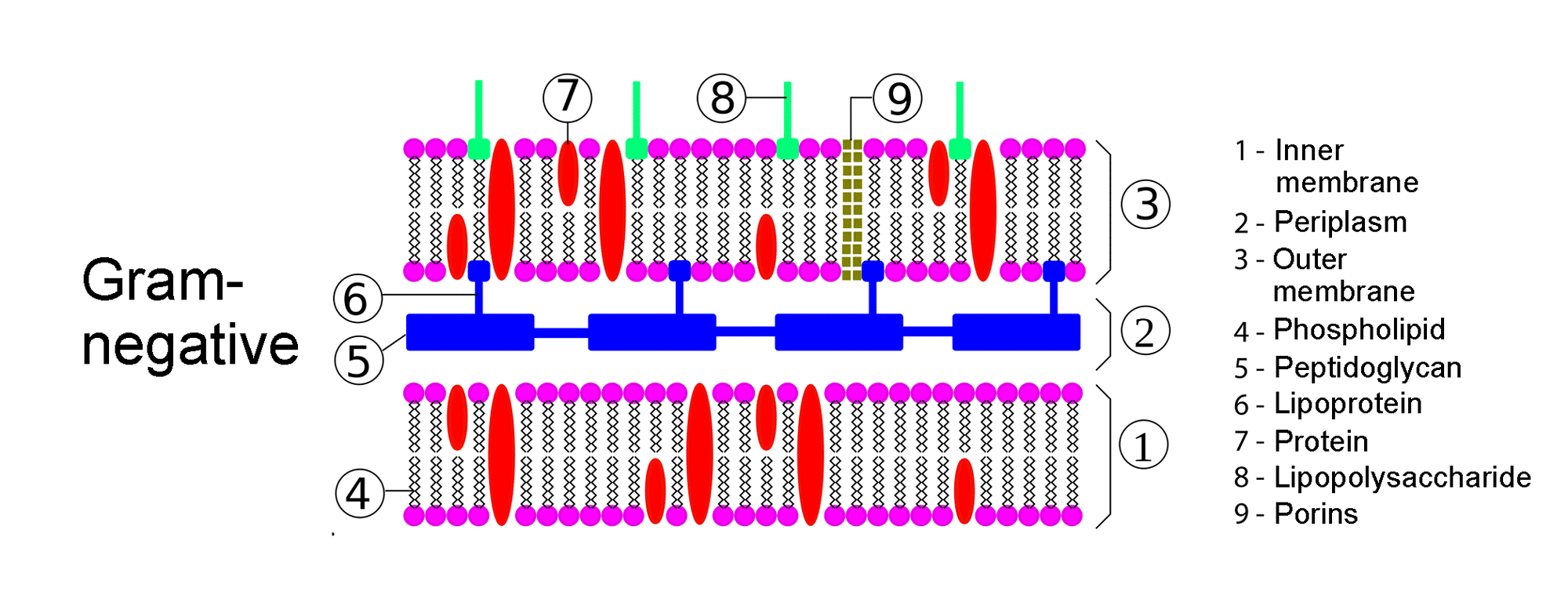
- Bacterium Gram “-”: These bacteria have three layers in the cell wall: The outer membrane composed of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides, the intermediate layer that is similar to the outer one of the Gram “+” but much thinner, and the inner cytoplasmic membrane the same as the inner membrane of bacteria Gram “+”.
The Advanced Oxidation Process (AOP) based on hydroxyl radicals can attack both types of bacteria. This is because both have chains of acids and proteins that are vulnerable to oxidation.
The oxidative reactions that occur cross the bacteria's membranes, modifying their morphological structure (eliminating the membranes), until reaching their genetic information, so that these irreversible damages kill and make the bacteria disappear.
To determine the effectiveness of OH technology against bacteria, various tests were carried out on air and surfaces, such as:
- Bacillus Subtilis:
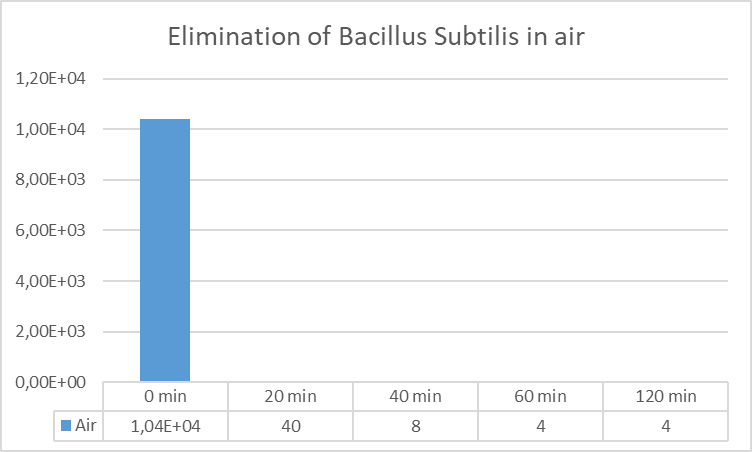 Graph 1. Decrease in the concentration of Bacillus Subtilis plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) in air.
Graph 1. Decrease in the concentration of Bacillus Subtilis plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) in air.
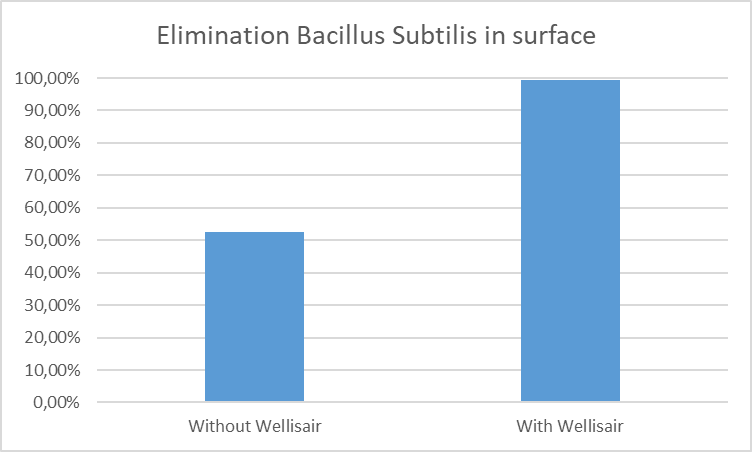 Graph 2. Decrease in the concentration of Bacillus Subtilis plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) on the surface 60 minutes after the start of the test.
Graph 2. Decrease in the concentration of Bacillus Subtilis plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) on the surface 60 minutes after the start of the test.
- Staphylococcus Aureus:
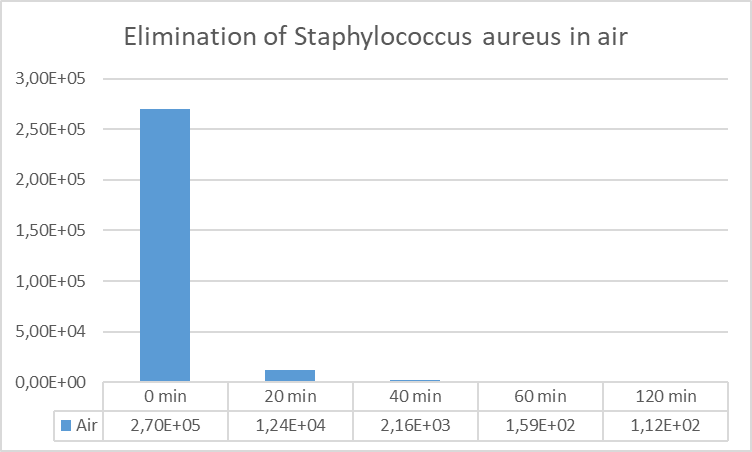 Graph 3. Decrease in the concentration of Staphylococcus Aureus plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) in air.
Graph 3. Decrease in the concentration of Staphylococcus Aureus plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) in air.
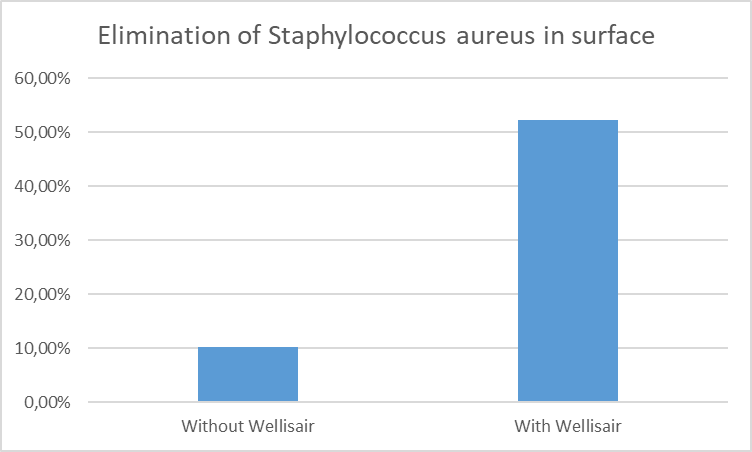 Graph 4. Decrease in the concentration of Staphylococcus Aureus plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) on the surface 60 minutes after the start of the test.
Graph 4. Decrease in the concentration of Staphylococcus Aureus plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) on the surface 60 minutes after the start of the test.
- Salmonella:
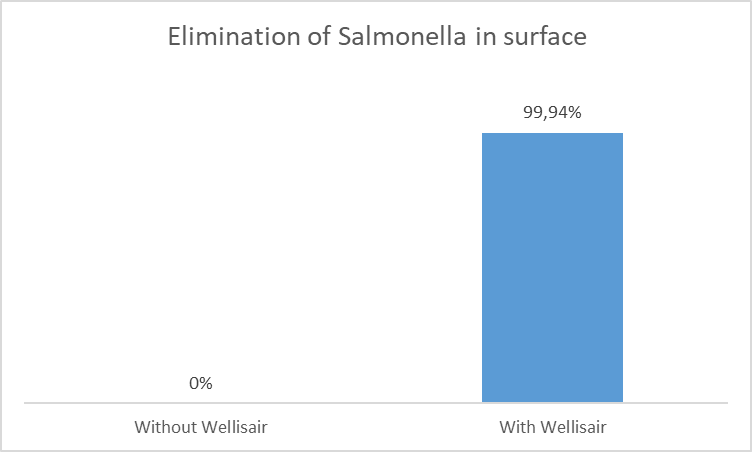 Graph 5. Decrease in the concentration of Salmonella plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) on the surface 4 hours after the start of the test.
Graph 5. Decrease in the concentration of Salmonella plaque forming units per millilitre (PFU / ml) on the surface 4 hours after the start of the test.
The results of these tests were very satisfactory, because, within a few hours of exposure, 99.9% of the bacteria were eliminated, both in air and on the surface.
